Every day, pulmonology practices handle procedures that range from routine to highly specialized. But when it’s time to bill, even the most experienced coders can find themselves asking, “Did I choose the right CPT code?” Bronchoscopies, biopsies, pulmonary function tests—each one has its own coding rules, and missing the smallest detail can mean a denial.
But what if you could break through the complexity and turn that confusion into clarity? With the right understanding of CPT codes, billing for pulmonology doesn’t have to feel like an uphill battle. Let’s take a closer look at the procedures you encounter every day and uncover how accurate coding can save both time and frustration.
Commonly Used CPT Codes For Pulmonology Procedures
Pulmonology involves a range of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to assess and treat conditions related to the respiratory system. From simple breathing tests to more invasive diagnostic procedures, the coding landscape is diverse.
1- Bronchoscopy (CPT 31622-31651)
Bronchoscopy is one of the cornerstone procedures in pulmonology, used for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. During a bronchoscopy, a physician inserts a flexible or rigid bronchoscope into the patient's airways—usually through the nose or mouth—to examine the lungs, airways, and sometimes to perform additional interventions. This procedure is crucial for diagnosing conditions such as lung cancer, infections, and airway obstructions.
Because bronchoscopies can involve several different techniques, a variety of CPT codes apply depending on the specific actions performed during the procedure:
CPT 31622:
This is the most basic code, used when a diagnostic bronchoscopy is performed. It involves inserting the scope to visually inspect the bronchial tubes and lungs. No additional interventions, such as biopsies or brushing, are included in this code. It’s commonly used when the goal is to identify abnormalities like tumors, inflammation, or obstructions.
CPT 31625:
This code is used when a biopsy is performed alongside the bronchoscopy. During a bronchial biopsy, the physician uses a special tool passed through the bronchoscope to take small samples of tissue from the bronchial walls. This tissue is then sent to a pathology lab to check for malignancies or other abnormalities, which is particularly useful in diagnosing lung cancer, infections, and inflammatory conditions.
CPT 31628:
This code covers a bronchoscopy with a transbronchial lung biopsy, which is a more invasive technique. Here, the physician collects tissue samples from the lung parenchyma (the functional part of the lung) by passing forceps through the bronchoscope. This code is often used when the doctor needs to examine deeper lung tissue to diagnose conditions like interstitial lung disease or sarcoidosis.
CPT 31628:
This code covers a bronchoscopy with a transbronchial lung biopsy, which is a more invasive technique. Here, the physician collects tissue samples from the lung parenchyma (the functional part of the lung) by passing forceps through the bronchoscope. This code is often used when the doctor needs to examine deeper lung tissue to diagnose conditions like interstitial lung disease or sarcoidosis.
CPT 31635:
This code applies when a bronchoscopic cryotherapy procedure is performed. Cryotherapy involves freezing and destroying abnormal tissue using a cryoprobe passed through the bronchoscope. It is used for treating certain tumors or obstructions in the airways.
Pulmonology Function Tests (PFTs) (94010-94770)
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs) are essential in diagnosing and managing respiratory conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and restrictive lung diseases.
These tests assess various aspects of lung function, including the volume of air a patient can exhale, the speed at which they exhale, and how well oxygen is transferred from the lungs to the bloodstream. Let's break down the key CPT codes associated with PFTs and what each one represents.
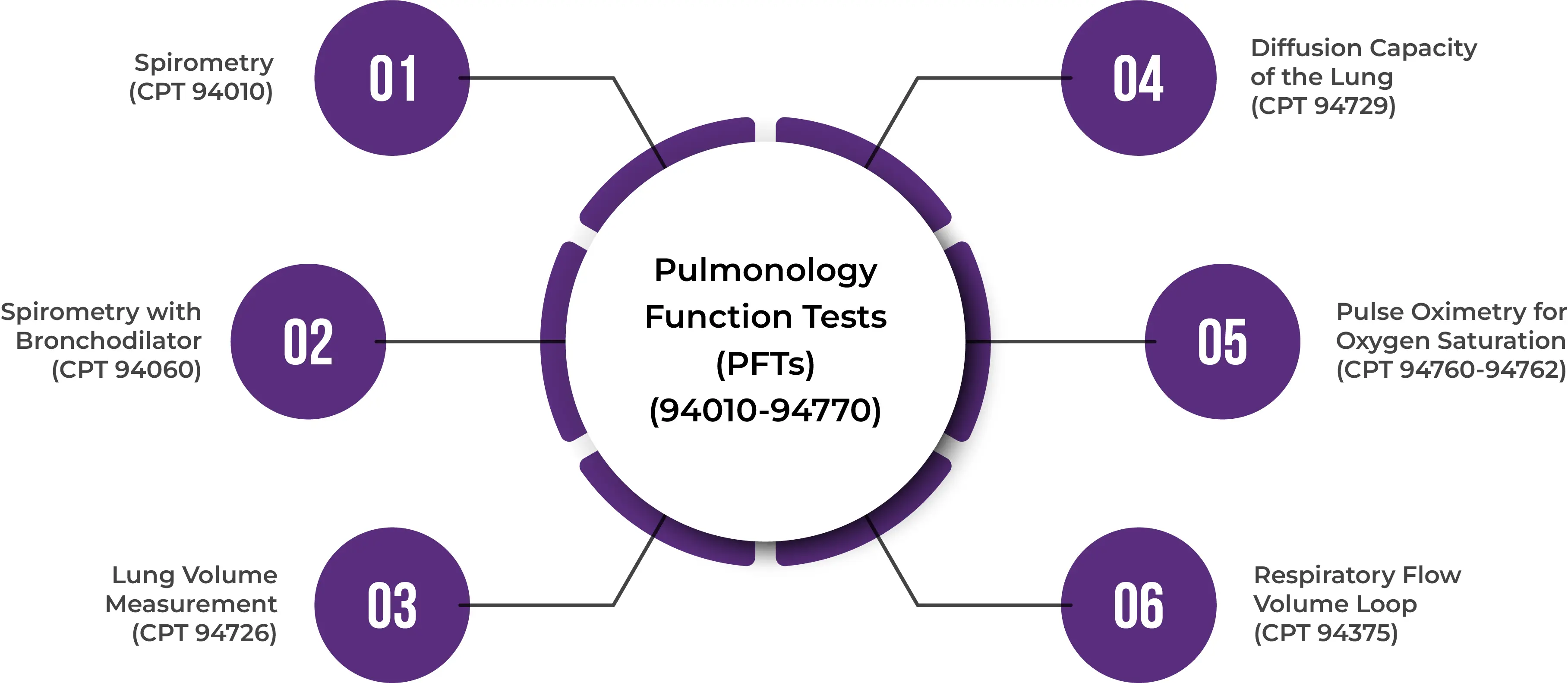
1. Spirometry (CPT 94010)
CPT 94010: This code is used for basic spirometry, a test that measures the volume and flow of air a patient can exhale. It evaluates lung function by measuring Forced Vital Capacity (FVC) and Forced Expiratory Volume in one second (FEV1). Spirometry is often the first step in diagnosing conditions like asthma or COPD.
2. Spirometry with Bronchodilator (CPT 94060)
CPT 94060: This code is used when spirometry is performed before and after the administration of a bronchodilator (such as albuterol) to assess how the patient's airways respond to the medication. It helps determine whether the patient has a reversible airway condition, which is often seen in asthma. This CPT is also billed for nebulizer treatment (inhalation treatment)
CPT 94060 is often billed in conjunction with CPT 94010 for the baseline spirometry reading, but make sure to follow payer guidelines for combining these codes.
3. Lung Volume Measurement (CPT 94726)
CPT 94726: This code is used for lung volume measurement using plethysmography or gas dilution techniques. Lung volume testing provides detailed information on the total capacity of the lungs and is particularly important in diagnosing restrictive lung diseases, where lung capacity is reduced (e.g., pulmonary fibrosis).
4. Diffusion Capacity of the Lung (CPT 94729)
CPT 94729: This code is used to measure the diffusion capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide (DLCO). The test assesses how well gases like oxygen pass from the air sacs in the lungs into the blood. It’s particularly useful in identifying diseases that affect the lung tissue itself, such as emphysema, pulmonary fibrosis, and pulmonary hypertension.
5. Pulse Oximetry for Oxygen Saturation (CPT 94760-94762)
CPT 94760: Used for non-invasive pulse oximetry, which measures the oxygen saturation of the blood using a small probe on the patient’s finger or earlobe. It’s a quick and easy way to assess how well oxygen is being delivered to the body. This code is typically used for spot-check oximetry.
CPT 94761: This code covers continuous pulse oximetry monitoring during procedures or over an extended period, often used in hospital or sleep study settings.
6. Respiratory Flow Volume Loop (CPT 94375)
CPT 94375: This code is used for a respiratory flow volume loop, which is a more detailed diagnostic test compared to standard spirometry. The flow volume loop provides a graphical representation of airflow during the entire respiratory cycle—both during forced inspiration and expiration. The test helps detect airway obstructions and assess conditions like asthma, COPD, and upper airway disorders.
Exercise Testing and Stress Testing in Pulmonology
Exercise testing is a valuable tool in pulmonology to assess how well the lungs, heart, and muscles respond to physical exertion. These tests help evaluate exercise tolerance, oxygenation, and heart function, and they are particularly important in diagnosing conditions like exercise-induced asthma, COPD, or pulmonary hypertension.
Six-Minute Walk Test (CPT 94618)
The six-minute walk test (6MWT) is a simple, non-invasive test used to assess a patient's functional exercise capacity. This test evaluates how far a patient can walk in six minutes, while also monitoring key parameters such as heart rate, oxygen saturation, and oxygen use. It is especially useful in assessing dyspnea (shortness of breath), exercise tolerance, and the effectiveness of interventions like supplemental oxygen.
-
CPT 94618: This code covers pulmonary stress testing, including the 6MWT, and includes the measurement of heart rate, oxygen saturation (using pulse oximetry), and oxygen titration during the test. The physician’s analysis and interpretation of the data (such as distance walked and the degree of oxygen desaturation) are included in the procedure.
Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing (CPT 94621)
For a more detailed analysis of lung and heart function under stress, cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) is performed. This test measures how well the respiratory and cardiovascular systems are functioning during increased physical demand. CPET is often used when diagnosing conditions like pulmonary hypertension, unexplained dyspnea, or to assess a patient's fitness before major surgery.
-
CPT 94621: This code is used for cardiopulmonary exercise testing, which includes:
-
Minute ventilation (the total amount of air inhaled and exhaled per minute),
-
CO₂ production,
-
O₂ uptake,
-
And electrocardiographic (ECG) monitoring during exercise.
-
Bronchial Provocation Testing (CPT 95070 & CPT 95071)
Bronchial provocation testing, also known as a methacholine challenge test or other challenge testing, is performed to evaluate airway responsiveness and diagnose conditions like asthma. This test involves exposing the patient to substances that may trigger bronchospasm (like methacholine, histamine, or other agents) and measuring the airway response. The purpose is to identify increased sensitivity in the airways, a hallmark of asthma or other reactive airway diseases.
-
CPT 95070: This code is used for inhalation bronchial challenge testing with an administered agent (e.g., methacholine or histamine), which assesses the patient’s airway responsiveness. It includes the administration of the agent but does not include the interpretation of the test results.
-
CPT 95071: This code is used for bronchial challenge testing with interpretation and report. In this case, the provider not only administers the challenge agent but also evaluates the test results, determining whether the patient experienced bronchospasm, and documents the findings in a formal report.
What is an unlisted pulmonary service or procedure?
When a pulmonary service or procedure does not have a specific CPT code, the provider should use an unlisted procedure code. These unlisted codes are designed to capture services that don't fall under any existing CPT codes.
CPT 94799: This is the unlisted code for unlisted pulmonary service or procedure. It is used when there’s no appropriate existing CPT code for a particular pulmonary function or respiratory service.
Final Words
Pulmonology coding, with its detailed procedures and complex CPT codes, can be challenging. Even small mistakes can lead to claim denials and delayed payments. If managing these codes feels like a burden, outsourcing your billing can make a huge difference. HMS USA LLC specializes in pulmonology billing, ensuring accuracy and maximizing your revenue. Let us handle the complexities so you can focus on patient care.
ABOUT AUTHOR

Tyler Rex
As a blog writer with years of experience in the healthcare industry, I have got what it takes to write well-researched content that adds value for the audience. I am a curious individual by nature, driven by passion and I translate that into my writings. I aspire to be among the leading content writers in the world.