Whether you're a healthcare provider diagnosing acute bronchitis or a medical coder responsible for precise documentation and coding, it's crucial to choose the correct ICD-10 code for proper reimbursement. Staying updated with the latest coding guidelines and information is paramount.
In this blog, we've compiled all the essential details you need to know about acute bronchitis, including its symptoms, coding guidelines, and the accurate Acute Bronchitis ICD-10 code. Join us as we delve into the intricacies of acute bronchitis coding, equipping you with the necessary knowledge to overcome any coding challenges confidently.
ICD-10 code for Acute Bronchitis
Common Symptoms for Acute Bronchitis
Different Types of Acute Bronchitis & ICD 10 Codes
What acute bacterial bronchitis icd 10 code
Acute bronchitis due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Acute bronchitis due to Hemophilus influenzae
Acute bronchitis due to streptococcus
Acute bronchitis due to viral infection
What is acute viral bronchitis icd 10?
Acute bronchitis due to coxsackievirus
Acute bronchitis due to parainfluenza virus
Acute bronchitis due to respiratory syncytial virus
Acute bronchitis due to rhinovirus
Acute bronchitis due to echovirus
Acute bronchitis with bronchospasm
icd 10 acute bronchitis with bronchospasm
Coding Guidelines for Acute Bronchitis
What is Bronchitis?
Bronchitis is a respiratory condition characterized by the inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which are the air passages that connect the lungs to the throat. It is often caused by viral infections, although bacterial infections or exposure to irritants like smoke or chemical fumes can also contribute to its development. The Bronchitis ICD 10 code normally used is J40.
Based on the duration of symptoms and specificity, bronchitis has been classified into two major types:
- Acute bronchitis
- Chronic bronchitis
ICD-10 code for Acute Bronchitis
According to the 10th edition of ICD-10, the billable ICD10 code for acute bronchitis is j20.9, effective from OCT 1, 2022. ICD 10 acute bronchitis j20.9 specifically refers to bronchitis without further specification.
Common Symptoms for Acute Bronchitis
The following are the most common symptoms of acute bronchitis it should be noted that these symptoms vary from person to person, and each person can experience these symptoms differently. Symptoms include:
Cough: A persistent cough is one of the primary symptoms of acute bronchitis. The cough may start dry and later produce mucus or phlegm.
Chest Discomfort: Individuals with acute bronchitis often experience chest discomfort or a feeling of tightness in the chest. This sensation may worsen during coughing episodes.
Shortness of Breath: Some individuals may experience difficulty breathing or shortness of breath, particularly during physical activity or exertion.
Fatigue: Acute bronchitis can cause fatigue and a general feeling of tiredness. This may be due to the body's efforts to fight off the infection.
Sore Throat: Inflammation and irritation in the bronchial tubes can extend to the throat, leading to a sore throat.
Mild Fever: A low-grade fever may be present in some cases of acute bronchitis. However, high fever is not typical and may indicate a more severe condition.
Different Types of Acute Bronchitis & ICD 10 Codes
In terms of ICD-10 codes, acute bronchitis is classified into different types based on the causative agent. Here are some common types of acute bronchitis and their corresponding ICD-10 codes.
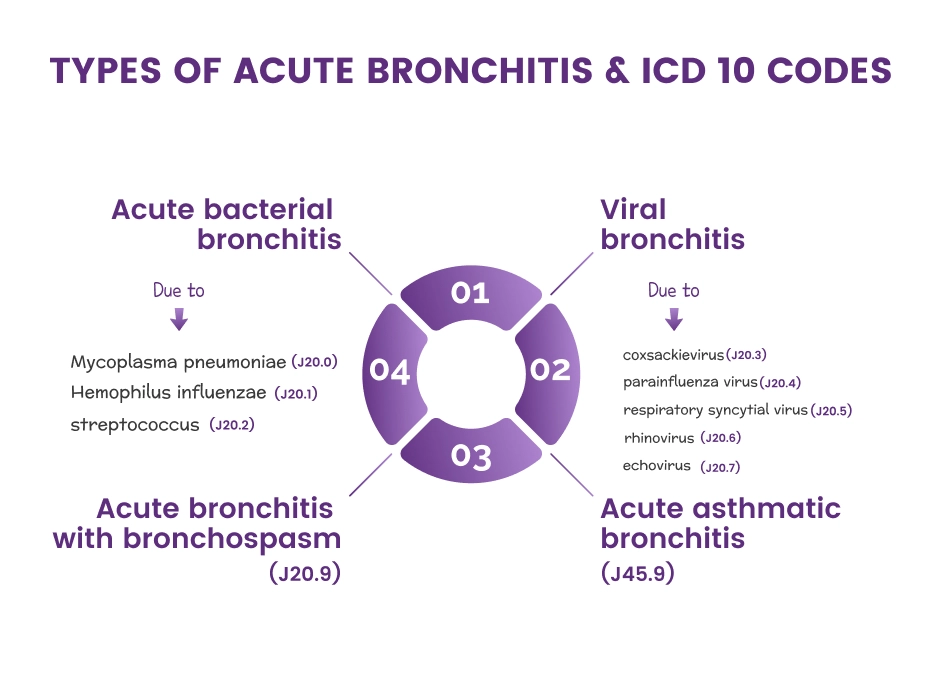
This type of acute bronchitis is caused by bacterial organisms. It may present with similar symptoms as viral bronchitis but may require specific antibiotic treatment.
What acute bacterial bronchitis icd 10 code
bronchitis due to bacterial infection is further categorized into different types, and it is recommended to use the specific acute bacterial bronchitis icd 10 code. However, J20.8 is used when Acute bronchitis is due to other specified organisms.
Acute bronchitis due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae
This is a specific type of acute bronchitis caused by the bacterium Mycoplasma pneumoniae J20.0 is used to diagnose Acute bronchitis due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Acute bronchitis due to Hemophilus influenzae
This is a specific type of acute bronchitis caused by the bacterium Hemophilus influenza. J20.1 is used to diagnose Acute bronchitis due to Hemophilus influenza.
Acute bronchitis due to streptococcus
Acute bronchitis due to Streptococcus is a specific type of acute bronchitis caused by the bacterium Streptococcus. J20.2 is used to diagnose Acute bronchitis due to streptococcus.
Acute bronchitis due to viral infection
Acute bronchitis due to viral infection is a common type of acute bronchitis caused by various viral pathogens. Viral infections, such as influenza viruses, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), rhinovirus.
What is acute viral bronchitis icd 10?
Like bacterial bronchitis, viral bronchitis is also further classified into different types and it is recommended to use the specific code.
Acute bronchitis due to coxsackievirus
Acute bronchitis due to Coxsackievirus is a specific type of acute bronchitis caused by the virus Coxsackievirus. J20.3 is used to diagnose Acute bronchitis due to coxsackievirus.
Acute bronchitis due to parainfluenza virus
Acute bronchitis due to Parainfluenza virus is a specific type of acute bronchitis caused by the virus Parainfluenza. J20.4 is used to diagnose Acute bronchitis due to parainfluenza virus.
Acute bronchitis due to respiratory syncytial virus
Acute bronchitis due to Respiratory syncytial virus is a specific type of acute bronchitis caused by Respiratory syncytial virus. J20.5 is used to diagnose Acute bronchitis due to respiratory syncytial virus.
Acute bronchitis due to rhinovirus
Acute bronchitis due to Rhinovirus is a specific type of acute bronchitis caused by the virus Rhinovirus. J20.6 is used to diagnose Acute bronchitis due to rhinovirus.
Acute bronchitis due to echovirus
Acute bronchitis due to Echovirus is a specific type of acute bronchitis caused by the virus echovirus. J20.7 is used to diagnose Acute bronchitis due to echovirus.
Acute bronchitis with bronchospasm
Acute bronchitis with bronchospasm is a specific type of acute bronchitis characterized by the presence of bronchospasm. Bronchospasm refers to the sudden narrowing of the airways, resulting in difficulty breathing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. In this condition, the bronchial tubes become constricted, making it harder for air to flow in and out of the lungs.
icd 10 acute bronchitis with bronchospasm
The ICD-10 code for acute bronchitis with bronchospasm is J20.9. This code is same as for acute bronchitis in an unspecified form.
Acute asthmatic bronchitis
Acute asthmatic bronchitis is a specific type of acute bronchitis that occurs in individuals with underlying asthma problems. acute asthmatic bronchitis icd 10 according to ICD-10 classification is J45.9.
Coding Guidelines for Acute Bronchitis
When accurately coding for acute bronchitis, it is important to follow specific coding guidelines to ensure comprehensive and precise documentation. Based on the provided content, here are the coding guidelines for accurately coding acute bronchitis:
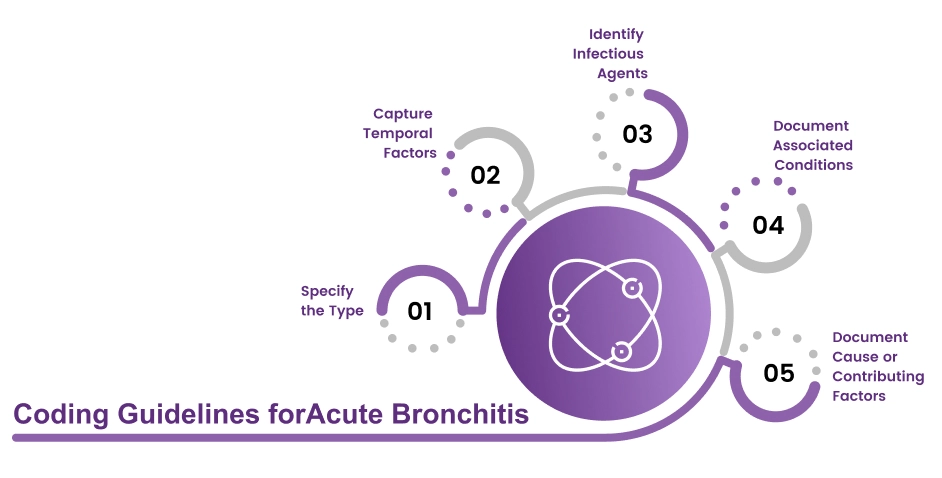
Specify the Type: Clearly document the specific type of bronchitis, such as simple, mucopurulent, fibrinous, membranous, purulent, or septic bronchitis. This information helps select the most appropriate ICD-10 code for the type of bronchitis present.
Capture Temporal Factors: Document the temporal factors related to the bronchitis, including whether it is acute, chronic, acute on chronic, or recurrent. These temporal factors play a role in code selection and accurately reflecting the duration and nature of the condition.
Identify Infectious Agents: Document the infectious agents associated with bronchitis whether these are viral or bacterial such as Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Hemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus, Coxsackie virus, Parainfluenza virus, Respiratory syncytial virus, Rhinovirus, Echovirus, or other specified organisms. This information helps select the appropriate ICD-10 code that reflects the specific causative agent.
Document Associated Conditions: Include any associated conditions such as tracheitis, tracheobronchitis, or bronchospasm in the documentation. These conditions should be documented to support medical necessity for the services rendered and may require additional ICD-10 codes.
Document Cause or Contributing Factors: Document any cause or contributing factors to the bronchitis, such as tobacco smoke exposure (occupational or environmental), tobacco dependence, tobacco use, or history of tobacco use. Assign additional ICD-10 codes to specify these factors and the bronchitis diagnosis code.
By adhering to these coding guidelines, healthcare providers and medical coders can accurately code for acute bronchitis, ensuring comprehensive documentation, appropriate reimbursement, and supporting the medical necessity for the services provided.
Final Words
In conclusion, accurate documentation and coding are essential when dealing with acute bronchitis. By understanding the symptoms and following the appropriate coding guidelines, healthcare providers and coders can ensure proper reimbursement and comprehensive documentation.
The ICD-10 code for acute bronchitis is J20.9, but it is important to specify the type, temporal factors, infectious agents, associated conditions, and cause or contributing factors to select the most appropriate code.
Remember to stay updated with the latest coding information to confidently navigate any coding challenges related to acute bronchitis.
ABOUT AUTHOR

Shahab Abbasi
As a blog writer with years of experience in the healthcare industry, I have got what it takes to write well researched content that adds value for the audience. I am a curious individual by nature, driven by passion and I translate that into my writings. I aspire to be among the leading content writers in the world.