As dedicated healthcare providers, you are well aware that precision coding is principal in accurately reflecting the services you offer. Yet, the complexity escalates when you find yourself entangled in the web of post-operative procedures, each with their own set of rules and guidelines.
When dealing with surgical procedure during the global period you are required to use the modifier 79. In this blog, we're here to guide you through the ins and outs of utilizing Modifier 79 effectively.
So read out this guide to get aware with the appropriate use of modifier 79 and how this aids towards accurate reimbursement.
Contents
Example Clinical Scenarios for Applying Modifier 79.
When to use modifier 79 in medical billing?
Difference between Modifier 78 vs 79
What are global periods?
A global period refers to the designated span of time during which all pre-operative, intra-operative, and post-operative services related to a specific procedure are bundled together for billing and reimbursement purposes.
In simpler terms, it encompasses the complete care package surrounding a surgical intervention, from the moment the procedure is initiated to the point at which the patient has fully recovered.
What is Modifier 79?
Modifier 79 is a defined as a procedure code that is used to indicate about an unrelated procedure was performed by the same physician during the post-operative period. In simpler terms it can be described as when a patient requires a procedure that is not directly associated with the initial surgery, but occurs within the global period, using Modifier 79 is essential.
By appending this modifier to the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code for the subsequent procedure, you communicate to payers that the service is distinct and separate from the prior surgical care.
How is Modifier 79 Applied?
In practice, the 79 modifier is appended to the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code of the second procedure. Appending modifier 79 signals to both payers and auditors that the subsequent procedure is independent and separate from the initial surgery.
This prompts a thorough review of the billing, allowing for accurate reimbursement that aligns with the complexity of the medical services provided.
One notable characteristic in the proper application of Modifier 79 is the association with different diagnoses. Typically, the second procedure should be linked to a diagnosis distinct from the one related to the original surgery.
Example Clinical Scenarios for Applying Modifier 79
Understanding the application of Modifier 79 in real-world clinical scenarios is instrumental in mastering its usage. Let's explore some example situations where this modifier proves its significance:
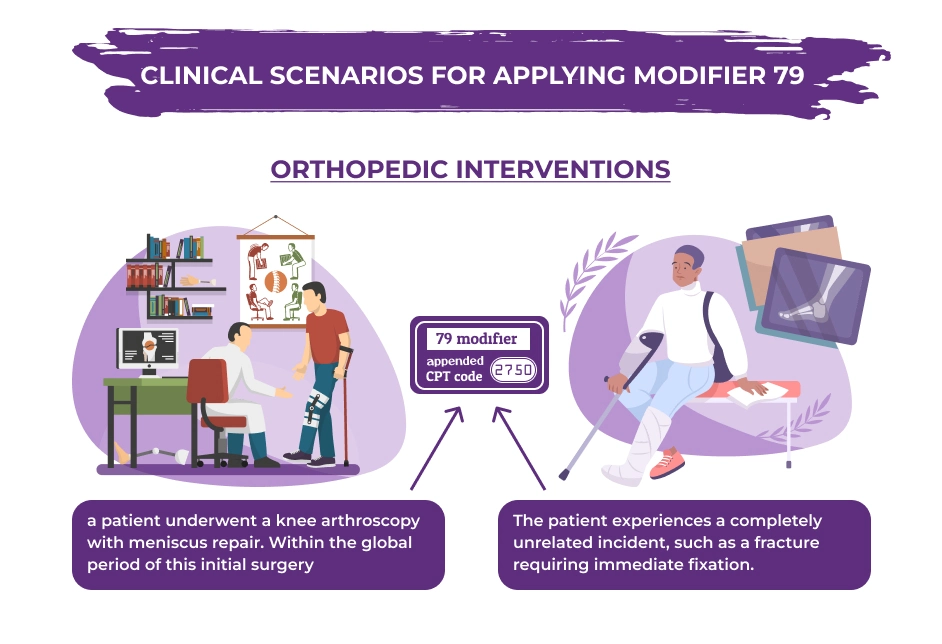
Orthopedic Interventions: Imagine a patient who underwent knee arthroscopy with meniscus repair. Within the global period of this initial surgery, the patient experiences a completely unrelated incident, such as a fracture requiring immediate fixation.
In this case, the 79 modifier would be appended to the CPT code for the fracture fixation procedure. The distinct nature of the procedures and the unrelated diagnoses would effectively communicate the need for separate billing to the payer.
Gastrointestinal Procedures: Suppose a patient undergoes a colonoscopy for diagnostic purposes and during the global period, an unforeseen complication necessitates an unrelated abdominal exploration. By using Modifier 79 with the CPT code for the abdominal exploration, healthcare providers indicate that the second procedure is distinct and unplanned, allowing for accurate reimbursement.
Dermatological Scenarios: Consider a scenario where a patient receives excision of a benign skin lesion, and subsequently develops an infection requiring drainage and debridement within the global period. Applying Modifier 79 to the drainage and debridement procedure underscores its separate nature from the initial excision and ensures proper billing for both services.
When to use modifier 79 in medical billing?
The strategic use of Modifier 79 in medical billing is important when facing scenarios that involve subsequent procedures performed during the global period of a prior surgery. This modifier serves to accurately communicate the independence of these subsequent procedures and to ensure appropriate reimbursement. Let's delve into when to use Modifier 79 to enhance your understanding of its application:
1. Unrelated Procedures: Modifier 79 comes into play when the subsequent procedure is entirely unrelated to the initial surgery. If a patient requires a new and distinct procedure that is not linked to the original surgical intervention, applying Modifier 79 is essential. This modifier indicates that the service is separate and should be billed independently from the initial surgery.
2. Unplanned and Essential Procedures: When unforeseen medical circumstances necessitate a subsequent procedure during the global period, Modifier 79 is a key tool. The modifier is appropriate when the second procedure is unplanned, unexpected, and vital for addressing a new medical concern that arises after the initial surgery.
3. Distinct Diagnoses: Applying Modifier 79 requires that the subsequent procedure is associated with a different diagnosis from the one linked to the original surgery. The distinction in diagnoses solidifies the need for separate billing, showcasing that the subsequent procedure caters to a separate medical issue.
4. Documentation of Medical Necessity: Before using Modifier 79, it's crucial to establish clear documentation of the medical necessity for the subsequent procedure. This documentation should illustrate why the procedure is distinct, unplanned, and unrelated to the original surgery. Such documentation substantiates the need for separate billing.
5. Preventing Unintended Bundling: Modifier 79 is a potent tool for preventing unwarranted bundling of services. It ensures that the subsequent procedure isn't mistakenly considered an integral part of the global period care, allowing for accurate billing that aligns with the complexity of the provided services.
Difference between Modifier 78 vs 79
While they may seem similar at first glance, they serve distinct purposes and are applicable under different circumstances. Let's delve into the differences between Modifier 78 and Modifier 79 to shed light on their respective roles:
Modifier 78: Unplanned Return to the Operating/Procedure Room by the Same Physician or Other Qualified Healthcare Professional Following Initial Procedure for a Related Procedure During the Postoperative Period
Usage: Modifier 78 is used when a patient requires an unplanned return to the operating or procedure room for a related procedure that is directly linked to the initial surgery. This related procedure is performed due to complications or issues arising from the initial surgery.
Key Characteristics:
- The subsequent procedure is related to the initial surgery.
- It involves the same patient and the same physician or qualified healthcare professional.
- The need for the subsequent procedure is due to complications, unforeseen issues, or incomplete aspects of the initial surgery.
- Modifier 78 is used to indicate that the subsequent procedure is part of ongoing care and is directly related to addressing issues from the initial surgery.
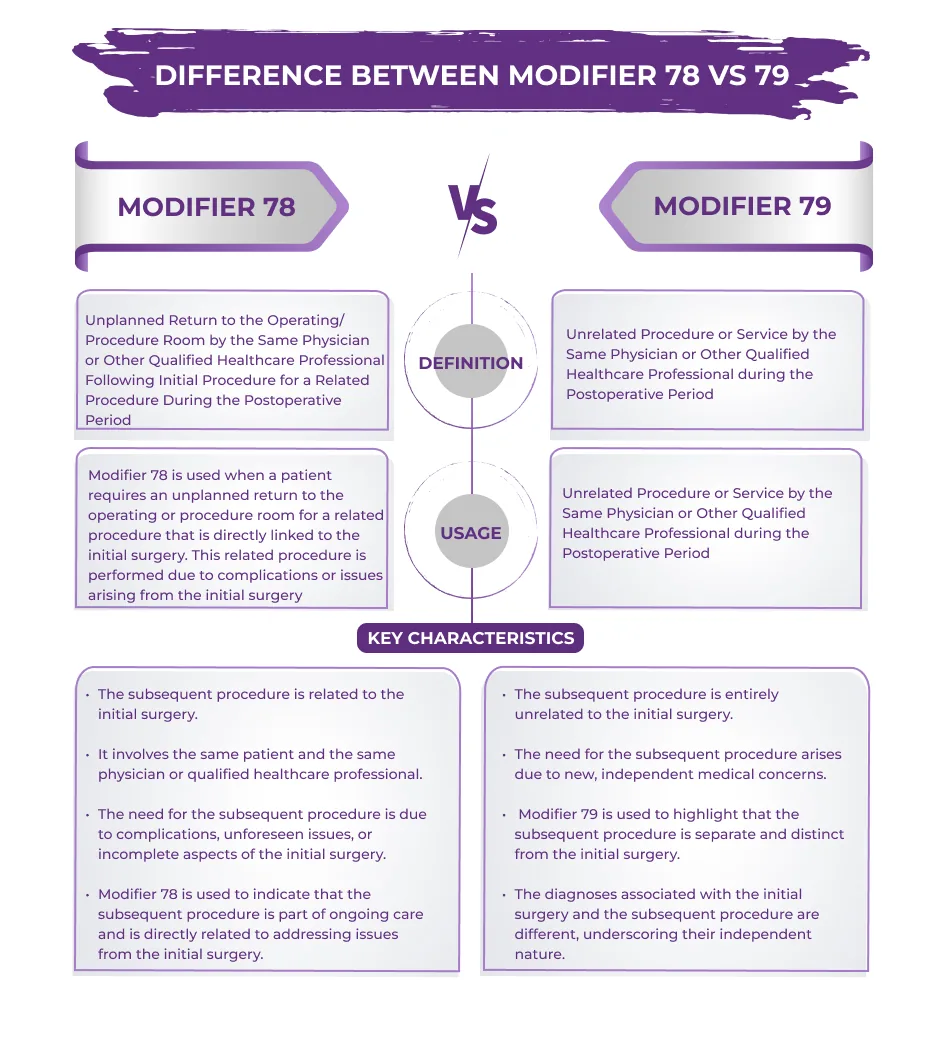
Modifier 79: Unrelated Procedure or Service by the Same Physician or Other Qualified Healthcare Professional during the Postoperative Period
Usage: Modifier 79 is employed when a patient requires an unrelated procedure or service during the postoperative period, which is not connected to the initial surgery.
Key Characteristics:
- The subsequent procedure is entirely unrelated to the initial surgery.
- The need for the subsequent procedure arises due to new, independent medical concerns.
- Modifier 79 is used to highlight that the subsequent procedure is separate and distinct from the initial surgery.
- The diagnoses associated with the initial surgery and the subsequent procedure are different, underscoring their independent nature.
Final Words
In last we can say that use of modifier 79 can be tricky and confusing for the provider but with the little guidance and clarification providers can excel the way, Modifier 79 emerges as a guiding beacon when dealing with subsequent procedures that deviate from the initial surgical path.
As healthcare providers, your commitment to accurate coding translates directly into accurate reimbursement. The strategic utilization of Modifier 79, in tandem with a clear understanding of its counterparts like Modifier 78, 58, and 76, positions you on the forefront of proper medical billing practice
ABOUT AUTHOR

Joe Black
As a blog writer with years of experience in the healthcare industry, I have got what it takes to write well researched content that adds value for the audience. I am a curious individual by nature, driven by passion and I translate that into my writings. I aspire to be among the leading content writers in the world.