In the world of medical billing and coding, Place of Service (POS) codes play a crucial role in accurately describing where healthcare services are provided to patients, a key component when filling out the CMS 1500 form.
These codes are used by healthcare providers when submitting claims to insurance companies for reimbursement. Understanding POS codes is essential for medical billers and coders as well as healthcare providers, insurance companies, and government agencies.
In this comprehensive guide, we will take a closer look at Place of Service codes, what they are, why they are important, and how to use them correctly.
What are Place of Service (POS) Codes?
Place of Service codes, also known as POS codes or POS modifiers, are two-digit numeric codes that describe the location where healthcare services were provided to patients. These codes were first developed by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) to standardize the reporting of healthcare services. They are now used by all insurance companies, including private payers, Medicare, and Medicaid.
POS codes are used to indicate the type of facility or setting where a patient receives care, such as a hospital, clinic, office, or home. They also specify whether services were provided in person, via telehealth, or through other means.
Why are Place of Service (POS) Codes Important?
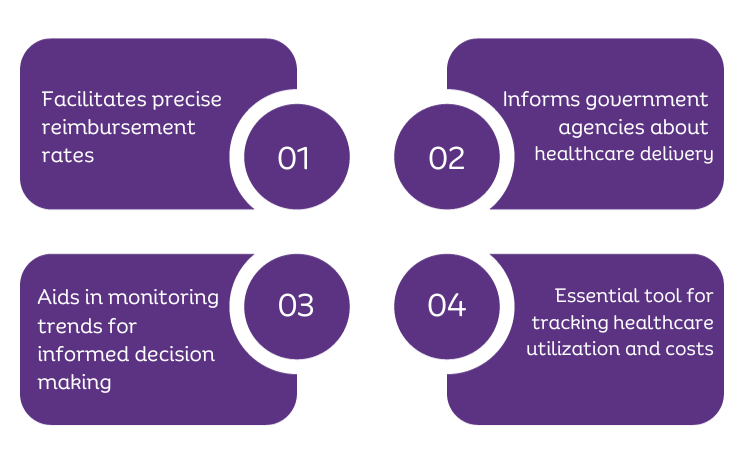
Accurate POS code reporting ensures precise reimbursement rates for different service settings and modes. It provides valuable insights to government agencies, aiding in informed decision-making and policy adjustments. POS codes are integral for tracking healthcare utilization, and identifying areas with high demand or potential fraud.
-
Facilitates precise reimbursement rates
-
Informs government agencies about healthcare delivery
-
Aids in monitoring trends for informed decision-making
-
Essential tool for tracking healthcare utilization and costs
Accurate POS code reporting is crucial for reimbursement accuracy and healthcare policy decision-making. It enables insurance companies to tailor reimbursement rates based on distinct service settings and modes. Government agencies benefit from the insights into healthcare delivery trends, aiding in informed decision-making. POS codes also play a crucial role in tracking healthcare utilization and costs, allowing the identification of areas with high demand or potential fraud.
How to Use Place of Service (POS) Codes Correctly
To utilize Place of Service (POS) codes accurately, grasp their structure—where the first digit denotes service category and the second specifies location or service type. For instance, place of service code 11 designates an Office, encompassing physician offices, clinics, group practices, and standalone facilities providing direct patient services.
Conversely, place of service code 22 denotes an On Campus-Outpatient Hospital, covering services in a hospital-based outpatient department where the patient is admitted as an outpatient.
-
POS code structure: First digit for category, second for location/type.
-
Example: POS code 11 represents an Office for direct patient services.
-
Choose POS based on the majority of services in a specific encounter.
-
Modify POS codes if the location changes during a single encounter.
Using POS codes correctly is crucial for accurate billing and reimbursement in healthcare. Understand their structure, assign based on service location, and be attentive to modifications if locations change during an encounter. Proper use ensures clarity in describing where healthcare services are delivered, benefiting insurance claims and policy decisions.
The Location-wise Application Process for POS Codes in Healthcare
Based on the location of service, POS codes can be grouped into four categories: Facility, Non-Facility, Telehealth, and Other.
1. Facility POS Codes
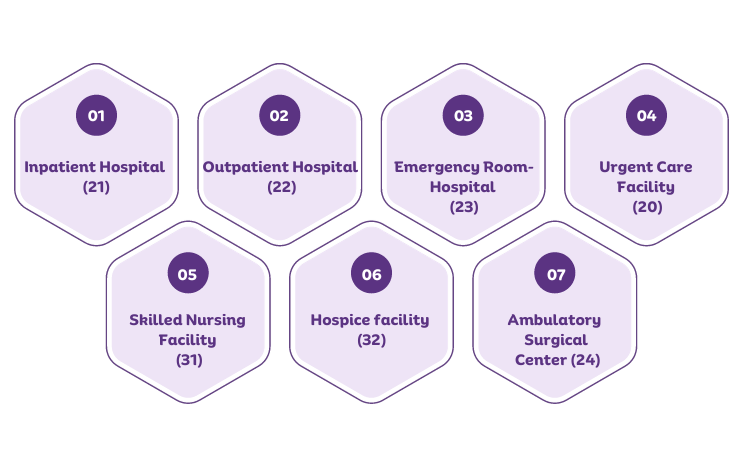
Facility POS codes are used to indicate services provided in a facility setting such as hospitals, nursing homes, or skilled nursing facilities. These include:
-
Inpatient Hospital (21)
-
Outpatient Hospital (22)
-
Emergency Room-Hospital (23)
-
Urgent Care Facility (20)
-
Skilled Nursing Facility (31)
-
Hospice facility (32)
-
Ambulatory Surgical Center (24)
These codes indicate that the services were provided in a facility that is owned and operated by a healthcare provider.
2. Non-Facility POS Codes
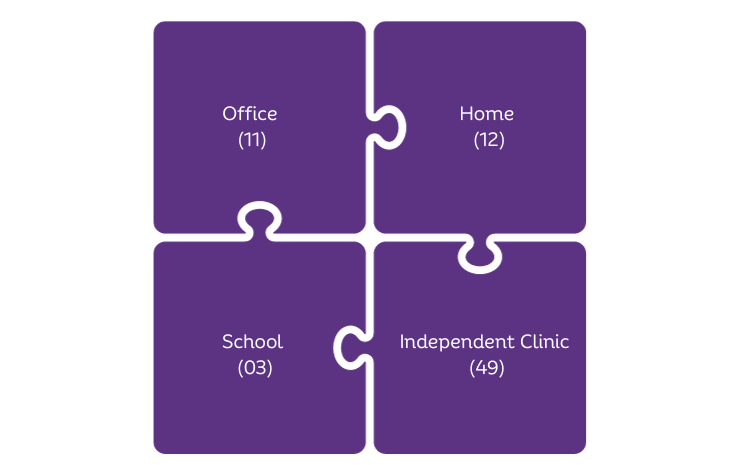
Non-facility POS codes are used for services provided in non-facility settings such as physician offices or independent clinics. These include:
-
Office (11) :
-
Home (12)
-
School (03)
-
Independent Clinic (49)
The above codes indicate that the services were provided in a setting not owned or operated by a healthcare provider.
3. Telehealth POS Codes
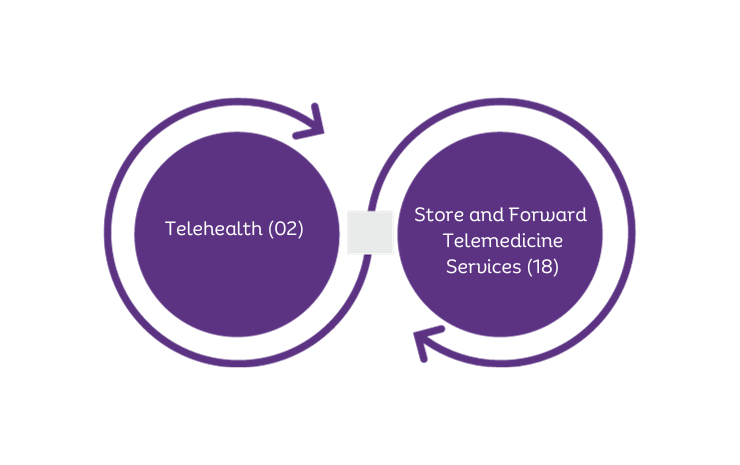
Telehealth place-of-service codes are used to indicate services provided through telecommunication technology. These include:
-
Telehealth (02)
-
Store and Forward Telemedicine Services (18)
This category of POS codes was introduced due to the increasing use of telehealth services in healthcare, and to differentiate them from traditional in-person services.
4. Other POS Codes
In addition to facility-specific POS codes, there are other codes that play a vital role in accurately describing healthcare encounters. These codes are designed for specific scenarios, such as visits to retail clinics, public health clinics, or rural health clinics. Each code serves a distinct purpose in the healthcare landscape.
-
Retail Clinic (17)
-
Homeless Shelter (04)
-
Rural Health Clinic (72)
These codes, including Retail Clinic (17), Home Shelter (04), and Rural Health Clinic (72), cater to unique healthcare settings, ensuring comprehensive coverage in billing and reporting. Understanding and applying these codes appropriately contributes to the precision of healthcare documentation and facilitates effective reimbursement processes.
Non-facility vs Facility POS Codes - What's the Difference?
The main difference between non-facility and facility POS codes is the payment structure. Non-facility POS codes have a lower reimbursement rate as they do not include any overhead costs associated with providing services in a facility setting.
On the other hand, facility POS codes have higher reimbursement rates to cover the additional expenses of running a facility. Therefore, it is important to select the correct POS code to ensure accurate reimbursement.
Final thoughts
Understanding Place of Service (POS) codes is vital in healthcare for standardized reporting, reimbursement accuracy, and cost tracking. This guide equips healthcare providers with essential knowledge, ensuring precise billing, and guarding against potential fraud. Stay vigilant for updates from insurance and government entities to uphold accurate documentation and billing practices in patient encounters.
Adaptability in the evolving landscape of healthcare, especially with advancing technology and the growing role of telehealth, is key. Providers should stay informed, aligning practices with industry changes for optimal care provision and billing adherence. Embracing the correct use of POS codes contributes to the overall efficiency of healthcare operations.
ABOUT AUTHOR

John smith
As a blog writer with years of experience in the healthcare industry, I have got what it takes to write well researched content that adds value for the audience. I am a curious individual by nature, driven by passion and I translate that into my writings. I aspire to be among the leading content writers in the world.
