You may be familiar that cardioversion is coded as an external and an internal procedure. When a patient reaches to you with an abnormal heartbeat, you know that it's time for a cardioversion, either the patient is under sedation or not.
Performing a cardioversion can be tricky sometimes as the providers are responsible for coding it accurately. This is important because cardioversion falls into a high-risk category and incorrect coding could lead to claim denials or even audits. So, let's dive in and learn about getting it right with the CPT code for cardioversion.
What is Cardioversion?
Cardioversion is a medical procedure that corrects an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia) by using an electrical shock. It can be done in two ways – either externally or internally.
External Cardioversion - A provider uses electrodes placed on the chest to deliver a synchronized electric shock to the heart. This type of cardioversion is also known as 'direct current cardioversion (DCC)'.
Internal Cardioversion - A provider inserts a small electrode catheter through a vein in the groin into the heart to deliver an electric shock. This type of cardioversion is also known as 'internal direct current cardioversion (IDCC)'.
External Cardioversion Vs. Internal Cardioversion
|
Feature |
External Cardioversion |
Internal Cardioversion |
|
Description |
A procedure where electrical shocks are applied to the chest wall using external paddles or patches. |
A procedure where the heart is electrically shocked using catheters placed inside the heart. |
|
Application |
Typically used for emergencies or outpatient treatment to restore normal heart rhythm. |
Often used during an electrophysiology (EP) study to terminate certain types of arrhythmias. |
|
Sedation |
Requires the patient to be sedated or under anesthesia for comfort. |
Generally requires sedation or anesthesia, especially if it's part of an EP study. |
|
Location |
Conducted on the skin's surface, over the chest. |
Conducted from within the heart chambers using intracardiac catheters. |
|
Intensity |
Typically requires higher energy levels due to the resistance of skin and chest wall. |
Uses lower energy since the shock is delivered directly within the heart. |
|
Advantages |
Rapid application in emergency situations; non-invasive. |
Precise treatment; can be used for specific arrhythmias not responsive to external cardioversion. |
|
Potential Risks |
Minor skin burns or irritations; risks associated with sedation or anesthesia. |
Risks associated with catheter placement; chance of clot dislodgement, sedation or anesthesia risks. |
Usage & Reimbursement rate of CPT Code 92960
92960 is the cpt code for electrical cardioversion and should always be reported as an isolated procedure. There are no specific codes or modifiers for the use of paddles or hands-free technology. It is important to note that it cannot be reported in the context of critical care. If a physician reports critical care time, they should instead report CPT codes 99291 and 99292.
In order to bill for this CPT code, it is necessary to inform the patient about the procedure and discuss the associated risks of the electrical cardioversion. Once the patient has signed a consent form, the healthcare provider can proceed with the elective cardioversion.
For example, A patient diagnosed with intermittent atrial fibrillation opts for an elective cardioversion to restore a normal heart rhythm. Before the procedure, the cardiologist explains the benefits and potential risks. The patient is then provided with a consent form to sign, ensuring they fully understand and agree to the procedure, emphasizing the necessity of patient consent for elective treatments. The fee for CPT code 92960 in a non-facility setting is $156.56 where as that for a facility setting is $108.01.
Usage & Reimbursement rate of CPT Code 92961
CPT 92961 is utilized for documenting internal cardioversion procedures. However, it should not be reported separately when it is performed as part of another procedure, such as an electrophysiological study or cardiac catheterization in a joint manner.
For example, if a patient has an internal cardioversion performed during a cardiac catheterization, code 92961 would not be reported separately.
It should be noted that two units for both CPT codes 92960 and 92961 can be reported on the same date of service, providers can bill 3 units if their documentation supports the medical necessity of the procedure. In Facility setting CPT Code 92961 is paid at $242.63.
What to code for Chemical Cardioversion?
Chemical cardioversion is a procedure where medications (often called antiarrhythmics) are used to restore a patient's heart to its normal rhythm. Unlike electrical cardioversion, where electrical shocks are applied, chemical cardioversion uses drugs to achieve the desired rhythm.
There is no specific CPT code for chemical cardioversion. Instead, infusion codes would be used to bill for the administration of medication. When conducted in a facility setting, it should be reported as an infusion. On the other hand, physicians are limited to using E/M codes or ECG for billing purposes.
What to code for Defibrillation?
The specific CPT code for cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is 92950, which encompasses a range of services. Notably, there isn't a standalone CPT code for defibrillation; it's included within the umbrella of CPR services.
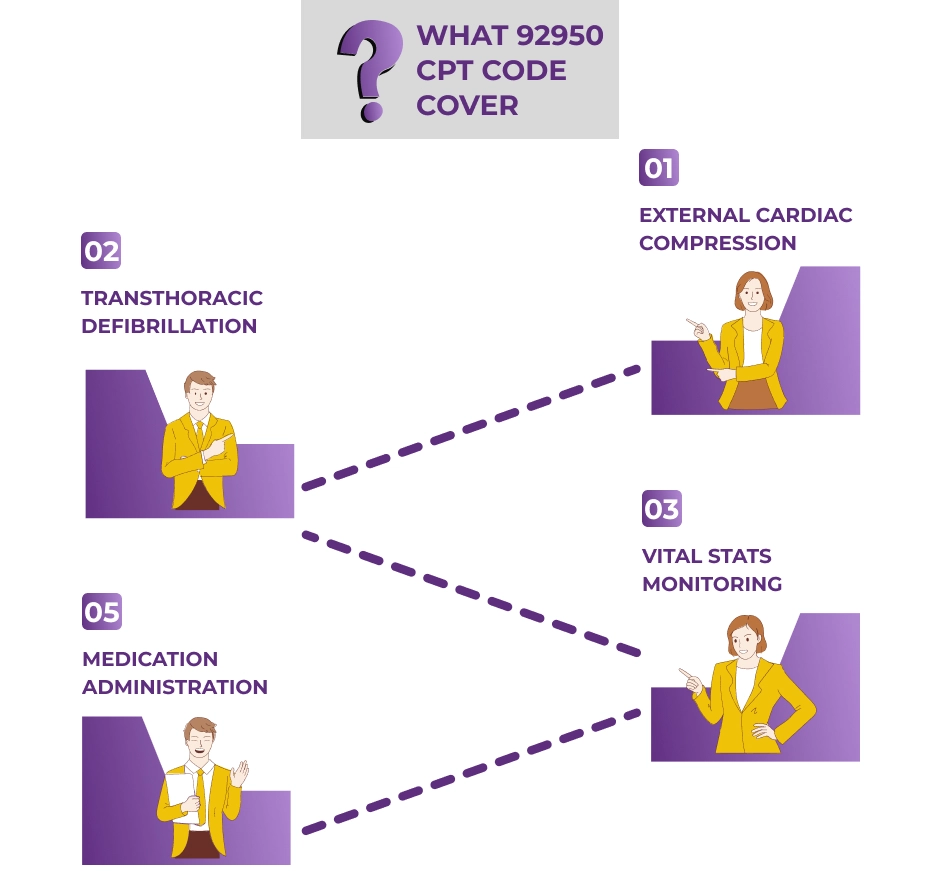
92950 CPT Code Description
CPT code 92950 covers:
-
External cardiac compression, potentially combined with ventilation during CPR.
-
External transthoracic defibrillation.
-
Continuous monitoring of vital stats and heart rhythm.
-
Administration of medications and fluids during the resuscitation process.
If defibrillation is executed in the absence of CPR, particularly in emergency department settings or critical care units, it's not billed separately.
Here's when you'd employ CPT code 92950:
-
If a patient experiences an observed cardiac arrest, CPR is undertaken. Following defibrillation, the heart rhythm normalizes.
-
Upon witnessing a cardiac arrest, CPR is started on a patient. Multiple defibrillation attempts occur, but the heart rhythm remains irregular.
-
For an unobserved cardiac arrest, a patient is discovered pulseless and non-responsive. Post-CPR and defibrillation, the heart rhythm stabilizes and the patient is rushed to a medical facility.
Conclusion
In summary, accurate coding for cardioversion procedures is essential for proper reimbursement and to maintain proper documentation of the patient's medical record. By understanding the different types of cardioversion and their associated CPT codes, healthcare providers can ensure that they are correctly coding and billing for these procedures.
If you are facing problems in managing your cardiology medical billing services, you can consider the expertise of HMS USA LLC. HMS is an experienced medical billing company that specializes in cardiology billing services. With their knowledge and expertise, they can help you accurately code for cardioversion procedures, ultimately leading to improved reimbursement rates and overall revenue for your practice.
ABOUT AUTHOR

Shahab Ud Din
As a blog writer with years of experience in the healthcare industry, I have got what it takes to write well researched content that adds value for the audience. I am a curious individual by nature, driven by passion and I translate that into my writings. I aspire to be among the leading content writers in the world.